12 Rainwater Harvesting Techniques for Families That Save Money Every Season
Discover practical rainwater harvesting techniques for your family – from simple rain barrels to advanced systems. Save money, conserve water, and create a sustainable future for your home.
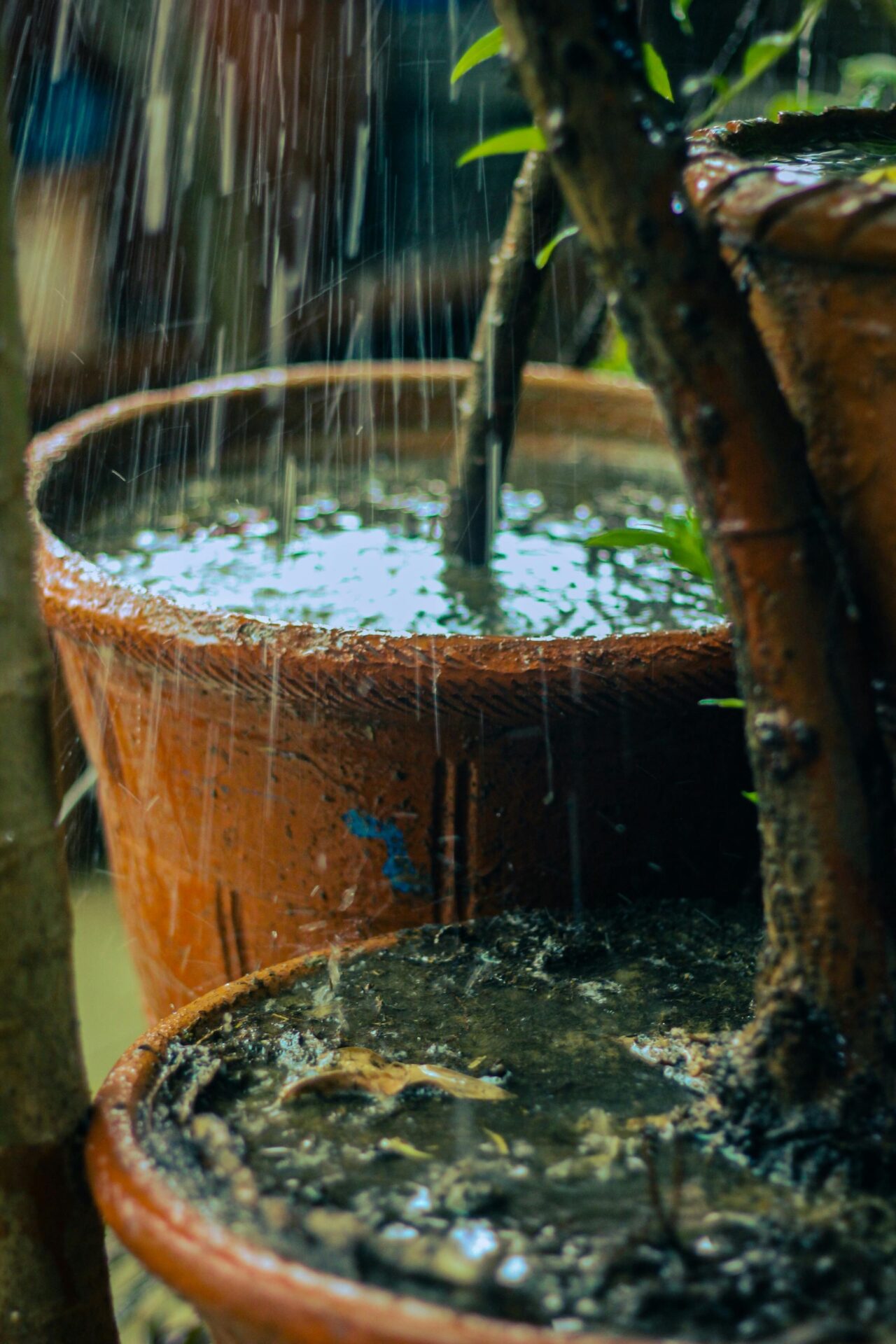
With water scarcity becoming a global concern, rainwater harvesting offers a sustainable solution that can help you reduce your household’s environmental impact while saving money on utility bills. By collecting and storing rainwater from your roof you’ll have access to a free natural resource that’s perfect for gardening watering lawns and even some indoor uses.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or already familiar with eco-friendly practices implementing a rainwater harvesting system doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. From simple rain barrels to sophisticated underground storage tanks you’ll discover that there’s a collection method perfect for your family’s needs and budget.
Disclosure: This site earns commissions from listed merchants at no cost to you. Thank you!
Understanding the Basics of Rainwater Harvesting
What Is Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a practical method of collecting rainwater from surfaces like roofs and storing it for later use. The process involves three main components: a catchment area (typically your roof) gutters and downspouts and storage containers. This system can range from simple rain barrels to complex filtration setups designed to capture thousands of gallons during rainfall events.
Benefits for Family Use
Implementing rainwater harvesting offers multiple advantages for your household’s daily needs. You’ll see immediate savings on water bills while creating a reliable backup water supply for emergencies. The collected water is perfect for garden irrigation laundry toilet flushing and car washing. Plus rainwater is naturally soft and free from added chemicals making it ideal for plants and reducing appliance wear.
Legal Considerations
Before setting up your rainwater system check local regulations as collection laws vary by state and municipality. Some areas offer tax incentives while others have specific requirements for system design and usage. Common regulations include proper mosquito prevention measures overflow management and backflow prevention devices. Contact your local water authority or building department to understand specific requirements for your area.
Installing Basic Rain Barrel Systems
A rain barrel system offers an efficient way to collect and store rainwater for household use.
Selecting the Right Rain Barrel
Choose a food-grade barrel with a 50-65 gallon capacity for optimal collection. Look for UV-resistant materials like recycled polyethylene that prevent algae growth. Your barrel should include essential features like a debris screen overflow valve tight-fitting lid and spigot near the bottom. Select a color that matches your home’s exterior while considering darker shades help prevent algae. Ensure the barrel has a flat stable base for safety.
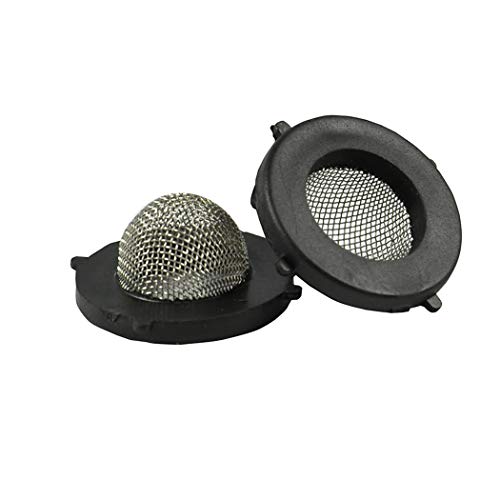
Danco hose washers provide a durable, leak-free seal for your 5/8-inch washing machine or garden hose. The built-in screen filters out debris, protecting your appliances and preventing clogs.
Setting Up Your First Collection System
Position your rain barrel on a level raised platform like concrete blocks or a sturdy stand. Connect the barrel to your downspout using a diverter or flexible downspout extension. Install the debris screen at the top to filter leaves twigs and mosquitoes. Attach the overflow valve near the top to direct excess water away from your foundation. Connect a garden hose to the spigot for easy access to collected water.
Maintaining Your Rain Barrels
Clean your barrel’s screen monthly to prevent debris buildup. Empty and rinse the barrel twice yearly using a mild soap solution. Check seals connections and spigots each season for leaks or damage. During winter drain the barrel completely and store it upside down to prevent cracking in freezing temperatures. Inspect the platform regularly to ensure it remains level and stable. Apply a vinegar solution quarterly to prevent algae growth.
Creating a Rooftop Collection System
A rooftop collection system forms the foundation of an effective rainwater harvesting setup. Here’s how to maximize your roof’s potential for water collection.
Calculating Your Roof’s Collection Potential
To determine your roof’s collection capacity multiply your roof’s square footage by your area’s average annual rainfall in inches then by 0.623 (the conversion factor for gallons). For example a 1500-square-foot roof in an area with 30 inches of annual rainfall can collect approximately 28035 gallons per year. Consider only the roof areas that drain to your planned collection points for accurate calculations.
Installing Proper Gutters and Downspouts
Install 5-inch or 6-inch seamless gutters with a minimum slope of 1/4 inch per 10 feet toward downspouts. Position downspouts at roof valleys and corners where water flow concentrates. Use 2×3-inch or 3×4-inch downspouts spaced every 30-40 feet of gutter length. Secure gutters with hidden hangers every 24 inches to prevent sagging under heavy rainfall.
Filtering Methods for Cleaner Water
Start with gutter guards to block large debris like leaves branches. Install a first-flush diverter to remove initial roof runoff containing dust bird droppings. Add a fine mesh filter (500-1000 microns) at the tank inlet to catch smaller particles. For drinking water use add a three-stage filtration system: sediment filter activated carbon filter UV sterilizer. Clean or replace filters according to manufacturer schedules.
Protect your home from water damage with Raptor Gutter Guards. This durable stainless steel micro-mesh kit fits 5-inch gutters and smaller, blocking leaves, pests, and debris while optimizing water flow with V-Bend Technology.
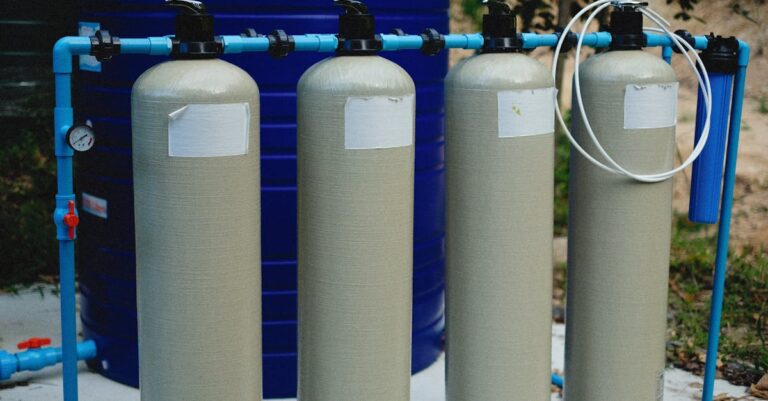
Building Underground Storage Solutions
Tank Size and Placement Guidelines
Calculate your tank size by multiplying your family’s daily water needs by the number of dry season days in your area. A typical family of four needs 100-150 gallons per day. Place tanks at least 50 feet from septic systems on flat stable ground with good drainage. Consider accessibility for maintenance monitoring sensors & overflow management. Install tanks below frost line depth for your region to prevent freezing.
Installation Steps for Storage Tanks
- Excavate the site 1-2 feet deeper than tank depth allowing for gravel base
- Create a 6-inch compacted gravel foundation pad
- Lower tank carefully using proper lifting equipment
- Install inlet piping filter systems & overflow valves
- Connect pump & electrical components
- Test system thoroughly before backfilling
- Backfill carefully in 12-inch layers using proper materials
- Grade soil for drainage away from tank
Pump and Filtration Systems
Install a submersible pump rated for your tank size & desired water pressure. Use a three-stage filtration system: sediment filter (50 micron) carbon filter (5 micron) & UV sterilizer for drinking water. Add a pressure tank to maintain consistent flow. Include check valves to prevent backflow & automatic shutoff for low water levels. Monitor filter condition monthly & replace as needed based on water quality & usage.
The MEDAS 1 HP Submersible Pump quickly removes water from pools, ponds, and basements. Its adjustable base handles clean or dirty water, and it can drain water to a minimal depth.
Implementing Smart Distribution Methods
Efficient distribution systems help maximize the benefits of your harvested rainwater while minimizing waste and maintenance needs.
Gravity-Fed Systems for Gardens
Set up gravity-fed irrigation by positioning your storage tanks at elevated points to create natural water pressure. Install a series of pipes with control valves at key locations throughout your garden beds. This simple yet effective system requires no electricity running costs maintains consistent water flow to your plants. Use 1-inch diameter pipes for main lines branching into smaller 1â2-inch tubes for individual plant zones. Add pressure-compensating drip emitters to ensure even water distribution across different garden elevations.
Automated Irrigation Setup
Install a smart irrigation controller connected to your rainwater system for precise watering schedules. Use moisture sensors in different garden zones to trigger watering only when needed. Program the controller to water during early morning hours reducing evaporation loss. Connect solenoid valves to separate garden zones allowing customized watering duration based on plant types. Include a rain sensor to automatically pause irrigation during rainfall preserving your stored water.
Indoor Usage Applications
Direct harvested rainwater to indoor non-potable applications through a dedicated plumbing system. Connect your rainwater tanks to toilet cisterns laundry machines & utility sinks using food-grade pipes. Install a pump with adequate pressure for consistent indoor water flow typically 40-60 PSI. Add a water level indicator to monitor tank levels & automatically switch to municipal supply when needed. Use separate color-coded pipes to distinguish rainwater from regular plumbing systems.
Maintaining Water Quality Standards
Ensuring the safety and cleanliness of harvested rainwater requires consistent monitoring and proper maintenance procedures.
Testing and Treatment Methods
Test your harvested rainwater every 3-6 months using water quality test kits to check pH levels bacteria content and contaminants. Install a UV sterilizer to eliminate harmful microorganisms and consider adding a carbon filtration system for improved taste and odor removal. Use chlorine tablets or food-grade hydrogen peroxide for disinfection at recommended concentrations (2-4 parts per million). Document test results and treatment dates in a maintenance log for reference.
Sanitize your salon tools and towels effectively with the ForPro Professional Collection UV Sanitizer. This 9L capacity machine features a built-in UV bulb with a 30/60/90 minute timer and includes two racks for optimal organization.
Safe Storage Practices
Store rainwater in opaque UV-resistant tanks to prevent algae growth and maintain consistent temperatures. Install vents with fine mesh screens to allow air flow while keeping insects out. Clean storage tanks annually using eco-friendly cleaners and maintain water levels above 20% to prevent sediment disturbance. Position tanks away from direct sunlight and heat sources to minimize bacterial growth. Label tanks clearly with “non-potable water” if not treated for drinking.
Enjoy fresh air and clear views with this durable 48"x102" fiberglass screen mesh. It's easy to install in windows, doors, and patios, providing lasting protection and ventilation.
Preventing Contamination
Install leaf guards and first-flush diverters on gutters to prevent debris from entering the system. Maintain a 6-foot distance between storage tanks and potential contamination sources like septic systems or chemical storage areas. Inspect and clean filters monthly replacing them according to manufacturer specifications. Use food-grade pipes and fittings for all plumbing connections and seal tank openings properly to prevent pest entry. Check roof surfaces quarterly for accumulated pollutants or damage.
Maximizing Collection Efficiency
Optimize your rainwater harvesting system’s performance with these essential maintenance practices and upgrades to ensure maximum water collection throughout the year.
Seasonal Maintenance Tips
Clean your gutters every spring and fall to remove leaves debris and twigs. Inspect downspouts quarterly for clogs or damage and clear any blockages immediately. Test your first-flush diverter monthly during rainy seasons to ensure proper operation. Sanitize storage tanks annually using a mixture of 1 cup bleach per 100 gallons of water. Check all seals gaskets and connections each season to prevent leaks that could reduce collection efficiency.
Overflow Management
Install multiple overflow outlets at different heights to manage excess water during heavy rainfall. Direct overflow pipes away from your home’s foundation toward rain gardens or swales. Use barrel connectors to link multiple storage tanks creating an automatic overflow system. Consider installing a water level indicator to monitor tank capacity and prevent overflow issues. Add larger diameter overflow pipes than inlet pipes to handle sudden water surges.
System Upgrades and Improvements
Add a pressure pump to improve water distribution throughout your system. Install automated first-flush diverters to reduce maintenance needs. Upgrade to larger capacity tanks when budget allows increasing storage potential. Consider adding UV filtration for expanded water use options. Implement smart monitoring systems to track water levels collection rates and usage patterns through mobile apps. Install additional collection points to maximize harvesting potential during light rainfall.
Integrating with Home Landscaping
Transform your yard into a water-efficient ecosystem that naturally captures and filters rainwater while enhancing your property’s aesthetic appeal.
Rain Gardens and Bioswales
Create a rain garden by designing a shallow depression in your yard to collect runoff from downspouts and hard surfaces. Select native plants like Black-Eyed Susans Coneflowers or Switchgrass that thrive in both wet and dry conditions. Position the garden at least 10 feet from your home’s foundation and size it to about 20% of your roof’s drainage area. Install bioswales along property slopes to direct water flow and prevent erosion using river rocks and deep-rooted vegetation.
Permeable Surfaces
Replace traditional concrete or asphalt with permeable alternatives to maximize groundwater recharge. Install pervious pavers for driveways which can absorb up to 3-5 inches of rain per hour. Use gravel paths bordered with recycled plastic edging for walkways. Add permeable concrete for patios which allows water to seep through while maintaining a solid surface. These surfaces reduce runoff by up to 80% compared to traditional materials.
Natural Filtration Methods
Incorporate natural filters to purify rainwater before storage or groundwater recharge. Plant buffer strips of native grasses and sedges around collection areas to trap sediment and pollutants. Create a rock-lined channel filled with varying sizes of gravel to filter debris and contaminants. Add aquatic plants like Cattails and Rush in wet areas to absorb excess nutrients and heavy metals. This three-tiered approach removes up to 90% of common pollutants from rainwater.
Teaching Children About Conservation
Getting children involved in rainwater harvesting creates lifelong environmental stewards while making conservation fun and engaging for the whole family.
Family-Friendly Projects
Transform rainwater collection into exciting hands-on projects kids will love. Create a mini rain gauge from recycled containers to measure rainfall amounts. Build a simple rooftop collection model using gutters and downspouts on a dollhouse or playhouse. Design colorful rain barrel decorations using weather-resistant paints to make conservation visually appealing. Start a water-saving garden where children can use collected rainwater to nurture their own plants.
Educational Activities
Make learning about water conservation interactive and memorable. Track weekly rainfall patterns in a weather journal using simple charts and graphs. Calculate how much water your family saves monthly through rainwater harvesting. Create a water cycle demonstration using a clear container terrarium with collected rainwater. Host family challenges to identify new ways to use harvested rainwater around your home like watering indoor plants or washing outdoor toys.
Monitoring Water Usage
Engage children in tracking household water consumption through hands-on activities. Install a simple water meter reader on your rain barrel spigot to measure daily usage. Create a family scoreboard to document weekly water savings from rainwater versus tap water. Use kid-friendly apps or charts to record and compare water usage patterns across different seasons. Reward conservation milestones with eco-friendly prizes or special activities using saved rainwater.
Conclusion: Sustainable Water Management for Families
Starting your rainwater harvesting journey is a practical step toward environmental stewardship and financial savings. You’ll find that the initial investment quickly pays off through reduced water bills and a more sustainable lifestyle.
Whether you’re starting with a simple rain barrel or planning a comprehensive underground system you’re contributing to water conservation while securing your family’s water independence. The techniques and methods shared here will help you create an efficient and reliable water collection system.
Remember that successful rainwater harvesting is an ongoing journey. You’ll need to maintain your system regularly adapt it to your changing needs and teach your family about responsible water usage. Take that first step today and join the growing community of families embracing sustainable water management.